Fast-track this part (max. 400 units) through our production facility. Shorten the delivery time by 1-2 working days. We are currently exclusively testing this delivery service for Germany.
incl. VAT
plus shipping costs
To cancel your filter settings again, click on the "Clear" button below the table.
You can display product details, including the eShop function and 3D model , by clicking in the row corresponding to the required article.
1. Product description
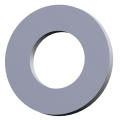
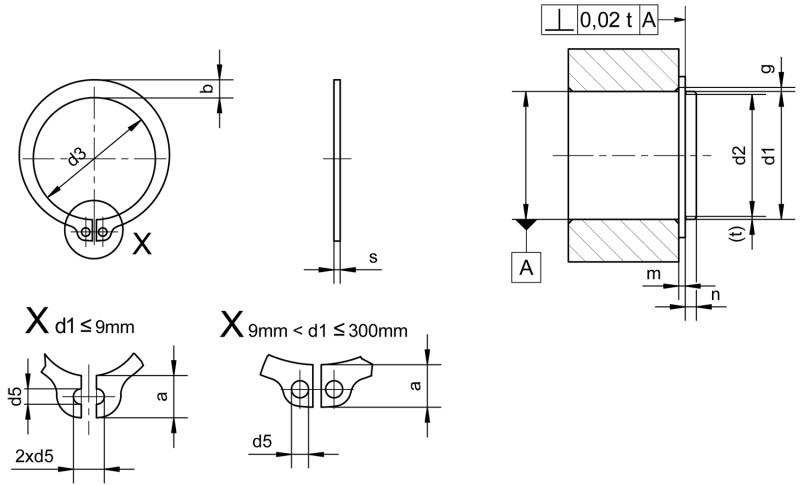
DIN 471 retaining rings, a fundamental component in the field of mechanical engineering, play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and integrity of assembled components. These rings are uniquely designed to secure bearings, gears, and other mechanical parts on shafts, axles, and bolts with groove, preventing them from slipping out of their seats. They are also suitable for transmitting axial forces.
These "external retaining rings" DIN 471, with outward-facing ends, are designed for shafts. Whereas "internal retaining rings" DIN 472 offer inward-facing ends and are used for assembly in a bore.
The design of DIN 471 retaining rings follows the specifications of the German Institute for Standardization (DIN). This ensures that each ring meets strict quality and dimensional standards, making them interchangeable and reliable in various machines and applications. The importance of these standardized components becomes particularly evident in complex machinery, where precise coordination between different parts is essential for smooth operation.
2. Product details
Size: 4 mbo 471 - 60 mbo 471
Material group: Steel, stainless steel
Surface: bright, electr. galvanised white, mech. galvanised silver, phosphatised oiled
3. Application Areas & Compatibility
Mechanical engineering: Retaining rings are frequently used in machines and systems for securing parts on axles, shafts, and bolts with groove to ensure precise positioning and to secure components against axial movement.
Heavy industry: In sectors such as mining, metal processing, and other heavy industries where machines are exposed to high loads, retaining rings play an important role in maintenance and ensuring mechanical integrity.
Electrical engineering and electronics: Retaining rings are also used in fine mechanical devices such as electric motors, switching devices, and household appliances to fasten components and ensure the system functions correctly.
Agricultural machinery: In tractors, combine harvesters, and other agricultural equipment, retaining rings help keep parts like bearings and drive elements securely in place, enabling smooth operation.
Medical technology: In some medical devices and instruments, retaining rings ensure the secure attachment of critical components, guaranteeing precision and reliability in their application.
Power generation: In power plants, including wind and solar energy facilities, retaining rings are used to secure components in generators and other critical systems.
Construction and architecture: Retaining rings are also employed in the construction of machines and equipment used in the construction industry and in some architectural structures.
4. Advantages and Benefits
Standardization and reliability: By adhering to the DIN 471 specifications, these retaining rings ensure high interchangeability and reliability across various applications and industries.
Flat design: Does not protrude much on the shaft and provides a secure fit in the groove.
Burr-free: Retaining rings according to DIN 471 must be burr-free, thus offering solid protection against injuries.
Wide range of applications: DIN 471 retaining rings are used in numerous sectors to secure components such as bearings and gears on shafts, axles, and bolts with groove.
Material diversity: Available in steel and stainless steel, these rings provide solutions for a variety of operating conditions, including corrosive environments, with stainless steel variants offering outstanding corrosion resistance.
Increased durability through surface treatments: Various surface treatments not only enhance the corrosion resistance but also the wear resistance of the rings.
Securing component position: They play a critical role by restricting the lateral movement of bearings and gears, thereby contributing to the integrity and reliability of mechanical systems.
Maintaining system functionality: Through precise construction and sizing, these rings ensure that mechanical systems remain functional and safe even under dynamic and stressful conditions.
Flexibility through comprehensive range of sizes: The broad variety of standard sizes allows for a precise fit in almost any application.
Increasing efficiency and safety in machine design: Engineers can design securely and efficiently because of the standard specifications and quality features of these components. In summary, retaining rings DIN 471 provide effective and secure fastening of mechanical components in a wide range of industrial applications thanks to their standardization, reliability, and versatile applicability.
5. Assembly and Installation
Step 1 - Preparation: Before starting the installation process, ensure you have all necessary tools. Typically, this includes an retaining ring pliers designed for DIN 471 retaining rings. These pliers have tips that fit into the small holes of the ring, allowing it to expand and mount onto the shaft. Also, check that the shaft and retaining ring are clean and free from any residues or lubricants, unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer.
Step 2 - Selecting the right size: Selecting the correct size of the DIN 471 retaining ring is crucial for a secure fit. The ring must match the diameter of the groove on the shaft where it will be installed. An incorrect size choice could result in the ring not securing properly or damaging the shaft. Groove diameter, groove width, and groove base must be matched to the retaining ring being used.
Step 3 - Opening the ring: Carefully insert the tips of the retaining ring pliers into the holes of the DIN 471 retaining ring. Gently squeeze the handles to open the ring. It's important to expand the ring only as far as necessary to avoid overexpansion or overstretching, which could potentially weaken the ring.
Step 4 - Positioning and mounting the ring: While the ring remains expanded, slide it over the end of the shaft and align it with the groove. Once it is properly aligned, slowly release the pressure on the pliers so that the ring can contract and snap into the groove. Ensure the ring sits evenly all around in the groove. An uneven fit can lead to premature failure.
Step 5 - Verifying the installation: After installing the ring, it's essential to check that it is securely seated in the groove. A well-mounted DIN 471 retaining ring exhibits minimal rotational movement and is flush with the groove walls. This verification is critical to prevent operational failures.
For axially mountable retaining rings that do not have installation holes, a cone-mounting provides the safest protection against overloading. For this, the ring is pushed over a pressure bolt or sleeve over a conical shape and thus brought into the groove.
6. Accessories
The suitable assembly pliers for the retaining rings DIN 471 can be found here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are retaining rings DIN 471 and why are they important?
What material are the DIN 471 retaining rings made of?
What surface treatments are available?
What areas of application are DIN 471 retaining rings typically used in?
What advantages do retaining rings DIN 471 offer?
How does the flexibility of the size series of retaining rings DIN 471 contribute to their application?
What tools are necessary for the installation of a retaining ring DIN 471?
What steps should be taken when installing a retaining ring DIN 471?
How can you ensure that the retaining ring DIN 471 is correctly installed?
What should be done if there are issues when installing DIN 471 retaining rings?
What is the difference between retaining rings DIN 471 and retaining rings DIN 472?
Retaining rings according to DIN 472 (internal retaining rings, with inward-facing ends), on the other hand, are intended for use in bores. They are installed in a groove within a bore and hold components in place from the inside out to prevent them from slipping out of the bore. Both types of retaining rings have a characteristic C-shape with ends that slightly point outward or inward, to facilitate insertion and removal with the help of a special retaining ring pliers. Despite their similar function and construction, they are designed for different applications, with DIN 471 used on the shaft and DIN 472 used in the bore.