Fast-track this part (max. 400 units) through our production facility. Shorten the delivery time by 1-2 working days. We are currently exclusively testing this delivery service for Germany.
incl. VAT
plus shipping costs
To cancel your filter settings again, click on the "Clear" button below the table.
You can display product details, including the eShop function and 3D model , by clicking in the row corresponding to the required article.
1. Product description
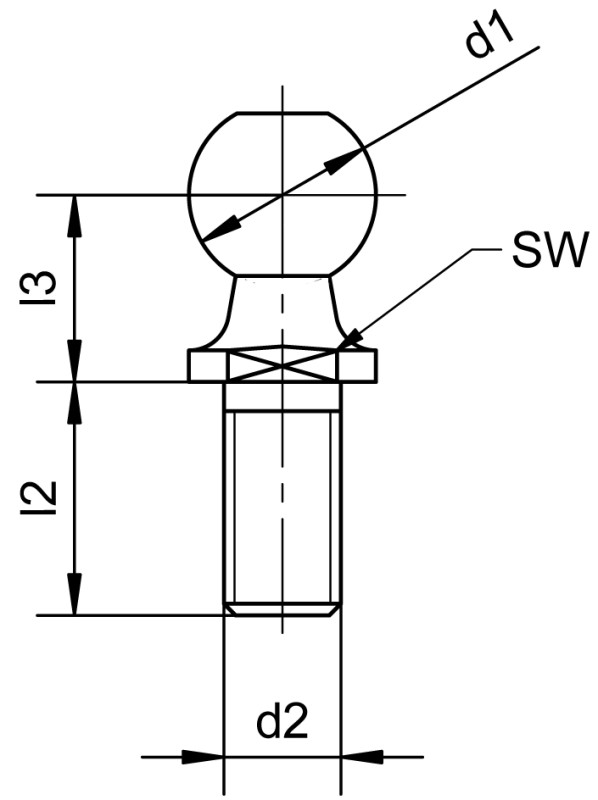
Ball studs conforming to DIN 71803 form C are mechanical linking elements designed to facilitate a flexible and precise connection in ball sockets. They consist of a cylindrical shaft with a threaded stud and a spherical head. These components ensure reliable power transmission and allow for high mobility in mechanical systems.
When mounted with a ball socket according to DIN 71805, ball studs according to DIN 71803 form an angle joint according to DIN 71802. Ball studs are available with threaded studs and spanner surface or as rivet studs (form B).
2. Product details
Size: C 6 M4 - C 19 M16
Material group: Steel, stainless steel, stainless steel A4 quality
Surface: bright, electr. galvanised white
Thread version: Regular thread right and left, fine-pitch thread right
d1 Ball diameter: 6 - 19
d2 Thread: M4 x 0,7 - M16 x 2
3. Application Areas & Compatibility
Mechanical engineering: In mechanical engineering, ball studs according to DIN 71803 are often used in movable linking elements and joints for control and power transmission. They are used in various types of machines such as machine tools, conveyor systems, and packaging machines. The high mobility and flexibility of the ball studs allow precise positioning and low-friction movements, reducing wear on other machine components and extending the lifespan of the entire system.
Vehicle construction: In vehicle construction, ball studs play a crucial role in steering linkages, suspension components, and other movable parts. They contribute to the stability and safety of the vehicles by enabling reliable power transmission and flexible movement. Especially in areas such as vehicle steering, suspension, and axle systems, ball studs are indispensable to ensure the necessary mobility and load capacity. They offer robustness and precision, which are required for the high demands in vehicle construction.
Robotics: In robotics, precise and flexible movements are of utmost importance. Ball studs are therefore integrated into joint systems to enable precise motion sequences and flexible connections. They are used in robotic arms, gripper mechanisms, and other movable parts that require precise positioning and controlled movements. The ability of ball studs to enable movements in multiple axes helps to increase the efficiency and accuracy of robotic applications.
Medical and rehabilitation technology: In medical and rehabilitation technology, ball studs are indispensable in movement mechanisms and medical devices. They enable gentle and precise movement, which is required in many medical applications. Examples include patient positioning systems or orthopedic devices. The ball studs help ensure exact and smooth movement, which is crucial for the safety and well-being of patients.
Construction and agricultural machinery: In construction and agricultural machinery, robust and durable connections are required to withstand extreme conditions and loads. Ball studs are used in various applications, such as on steering linkages and suspension systems. Their ability to absorb forces and enable movements in multiple axes makes them ideal for use in machines that are operated in harsh environments. They offer the necessary stability and flexibility to enhance the performance and lifespan of the machines.
Compatibility
Ball studs according to DIN 71803 are standardized components that guarantee high compatibility with other elements manufactured according to the same standards. They are compatible with ball sockets according to DIN 71805 and can be integrated into various applications and systems, which are also designed according to these standards. This significantly facilitates the exchange and integration into existing systems and ensures uniform quality and reliability of the connection elements. Mounted with a ball socket according to DIN 71805, ball studs according to DIN 71803 form an angle joint according to DIN 71802.
Custom designs: mbo Osswald also offers the possibility of manufacturing custom designs tailored to the specific requirements of the customer.
4. Advantages and Benefits
High freedom of movement: Ball studs according to DIN 71803 are designed to enable movements in multiple axes. This means they can support movements not only in a linear direction but also at various angles and rotations. This ability for multi-axis movement is particularly advantageous in applications requiring complex movements. For instance, in robotics, where precise and flexible movements are crucial, or in vehicle steering, where smooth and flexible control is necessary. The high freedom of movement increases the flexibility of the entire system, leading to improved functionality and performance.
Durability: The ball studs are robustly manufactured, giving them high load-bearing capacity and long lifespan. They are made from high-quality materials such as steel and stainless steel, known for their ability to withstand large forces and high mechanical stresses. Furthermore, the ball is hardened. These properties are especially important in applications where components are regularly exposed to high loads and vibrations, like in vehicle and machinery construction. The durable construction of the ball studs helps extend maintenance intervals and reduce operating costs, as they need to be replaced less frequently.
Corrosion resistance: Stainless steel versions of the ball studs offer excellent protection against corrosion, making them ideal for use in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive influences. This is particularly important in industries like medical technology, where hygienic conditions are essential, or in outdoor applications like construction and agricultural machinery, which are exposed to the elements. The corrosion resistance helps extend the lifetimes of the ball studs and increases the reliability and safety of the entire construction.
Standardization: Ball studs according to DIN 71803 are standardized, meaning they are manufactured to uniform specifications and tolerances. This standardization offers several advantages. Firstly, it ensures high compatibility with other standardized components, such as ball sockets according to DIN 71805, simplifying integration and replacement in existing systems. Secondly, standardization facilitates global trade and procurement, as components are manufactured and used everywhere according to the same quality standards. This ensures uniform quality and reliability of the connection elements and contributes to cost-efficiency since readily available components can be used instead of needing custom-made parts.
Low maintenance: Due to their robust construction, high-quality material selection, and hardened ball, ball studs are generally low maintenance. This means they need to be lubricated or replaced less frequently. This can be especially beneficial in hard-to-reach applications or in systems that operate continuously.
5. Assembly and Installation
Preparation: Before the assembly of ball sockets and ball studs begins, it is crucial to ensure that all components are clean and free from contaminants. Dirt, grease, or other foreign particles can impair the functionality and longevity of the connection. Therefore, ball sockets and ball studs should be well cleaned. A clean surface ensures a precise fit and prevents premature wear.
Assembly: The assembly of the ball stud begins with inserting it into the bore of the appropriate ball socket. The snap ring within pushes over the ball of the ball stud, fixing the stud in the socket. Care must be taken to avoid damaging the ball socket or the stud. It is important that all parts are properly and correctly seated to ensure the mobility of the stud within the socket and yet prevent it from loosening during operation.
Lubricant: To minimize friction and wear between the ball socket and ball stud, the use of a suitable lubricant is crucial. The lubricant should be evenly applied to the contact surfaces and ideally consist of high-quality grease or oil that is suitable for the specific application conditions. This helps to ensure smooth movement and extend the lifespan of the components. When selecting the lubricant, factors like temperature range, load, and environmental influences should be considered.
Tightening torque: When screwing the parts to be assembled, it is vital to pay attention to the recommended tightening torque. Too high a torque can lead to overloading and damaging the components, while too low a torque may inadequately secure the connection. Torque specifications are included in the relevant technical documentation or standards and should be strictly followed. To ensure accurate adherence to the torque, it is advisable to use a calibrated torque wrench. Correct torque ensures secure fastening and contributes to avoiding mechanical problems during operation.
Additional notes
Visual inspection: After assembly, all connections and fastening points should be visually checked for correct alignment and any possible assembly errors.
Retightening: It might be advisable to retighten the connections after some operating time to ensure that no parts have loosened.
Protective Measures: For applications in aggressive environments, additional protective measures such as sealing caps or special coatings should be considered.
These detailed steps and notes ensure the correct assembly and installation of ball sockets and ball studs and help ensure a long and reliable service life of the connections in various applications.
6. Safety instructions & Standards
Safety check
Regular safety checks are crucial to ensure the reliability and operability of ball studs and ball sockets. Special attention should be paid to signs of wear and any potential damages.
Visual inspection: Regular visual inspections of the ball studs for cracks, corrosion, and other damages.
Mechanical test: Check the clearance between the ball and the socket to ensure it does not exceed the permissible tolerances.
Function test: Check the freedom of movement of the ball to ensure it operates evenly and smoothly. Early detection of wear and damage allows for timely intervention, preventing failures or accidents during operation.
Compliance with standards
Adherence to the specifications and tolerances set forth in DIN 71803 is essential for ensuring the optimal performance and safety of the ball studs.
Dimensional tolerances: Strict compliance with the dimensional tolerances for ball sockets and studs as specified in the standard.
Material requirements: Use of prescribed materials to ensure the required strength and resistance.
Test reports: Documentation and verification of measurements and test results to ensure all components meet the standard requirements. By complying with these standards, it is ensured that the components function reliably and safely.
Load limits
The load limits of the ball studs and sockets should not be exceeded under any circumstances. This serves to prevent damage and failures.
Maximum load capacity: Adherence to the maximum permitted load capacity.
Dynamic loads: Consideration of not only static but also dynamic loads that may act on the component.
Safety factors: Application of an appropriate safety factor in the component design to account for unforeseen peak loads. By observing the load limits, the lifespan of the components can be maximized and safety increased.
These safety instructions and standards offer comprehensive guidance for the safe use and maintenance of ball studs and sockets, helping to minimize operational risks and ensure the longevity of the components.